MP4(或称MPEG-4第14部分)封装是我们日常生活中使用最多的封装方式之一,下面对MP4的格式进行简要介绍
MP4 File Structure
MP4的文件结构就像json,是由一个个容器相互包含而成
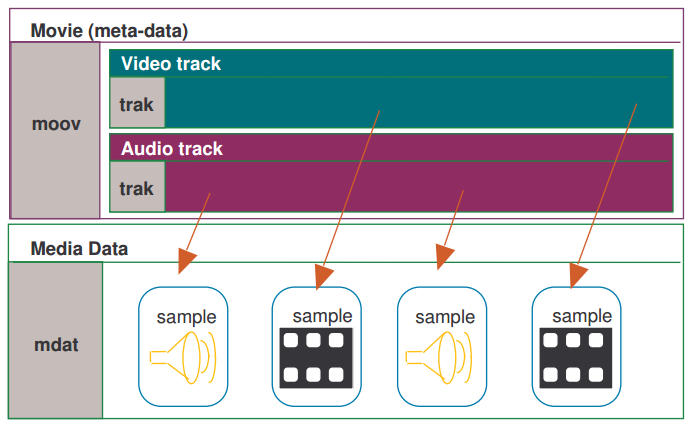
接下来我们就来分析一下这些容器,首先使用软件打开这个mp4文件:
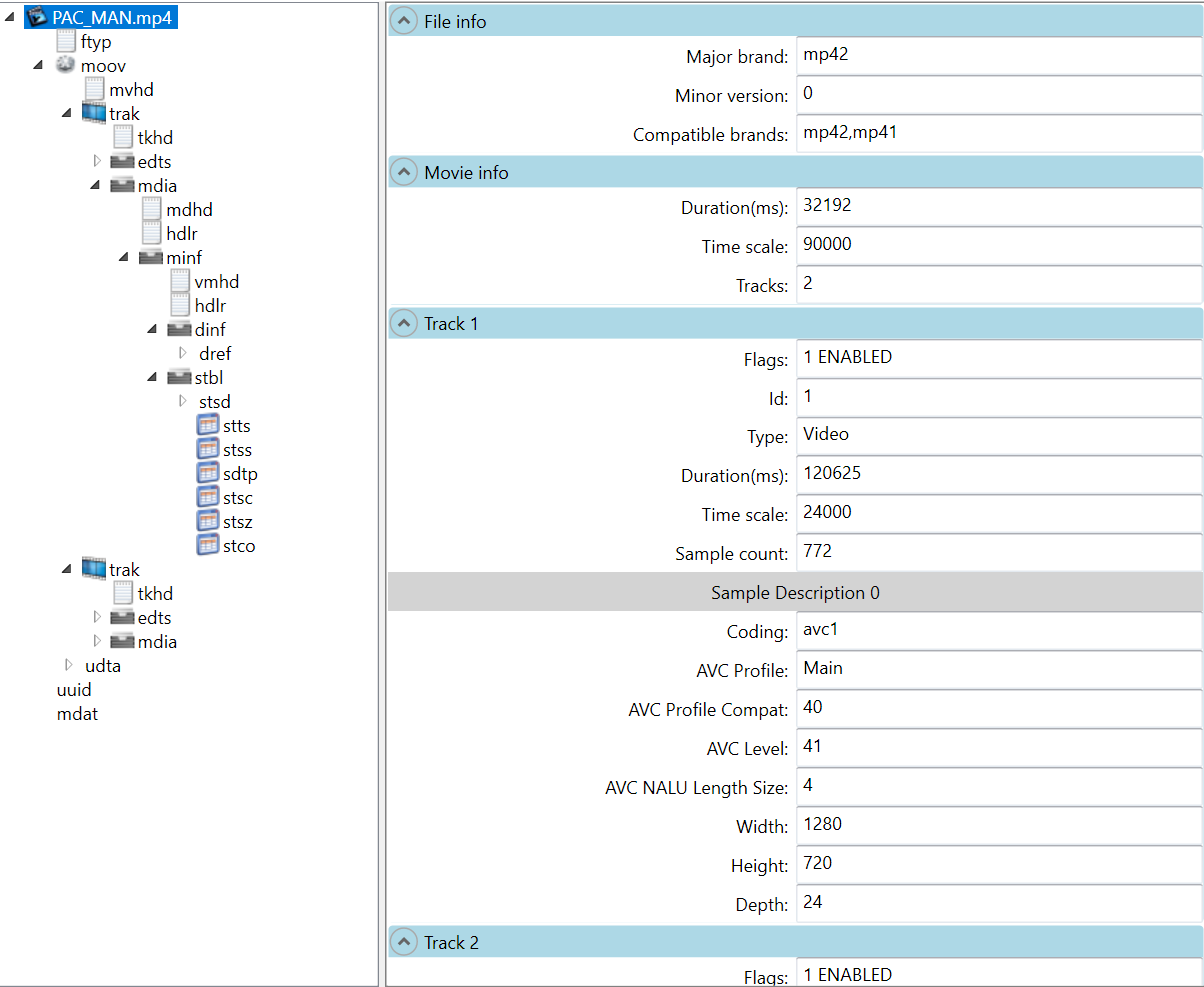
首先,解析一个 MP4 文件是这样的,刚开始的 0 ~ 3 字节是 box 的 size (大小),然后 4 ~ 7 字节是 box 的类型。从上图可以看出 PAC_MAN.mp4 的第一个 box 的大小 是 0x18 字节(包含头部),然后这个是 ftyp 类型的box,至于这 0x18 字节里面是什么内容 就按照 ftyp 类型去解析就行了。
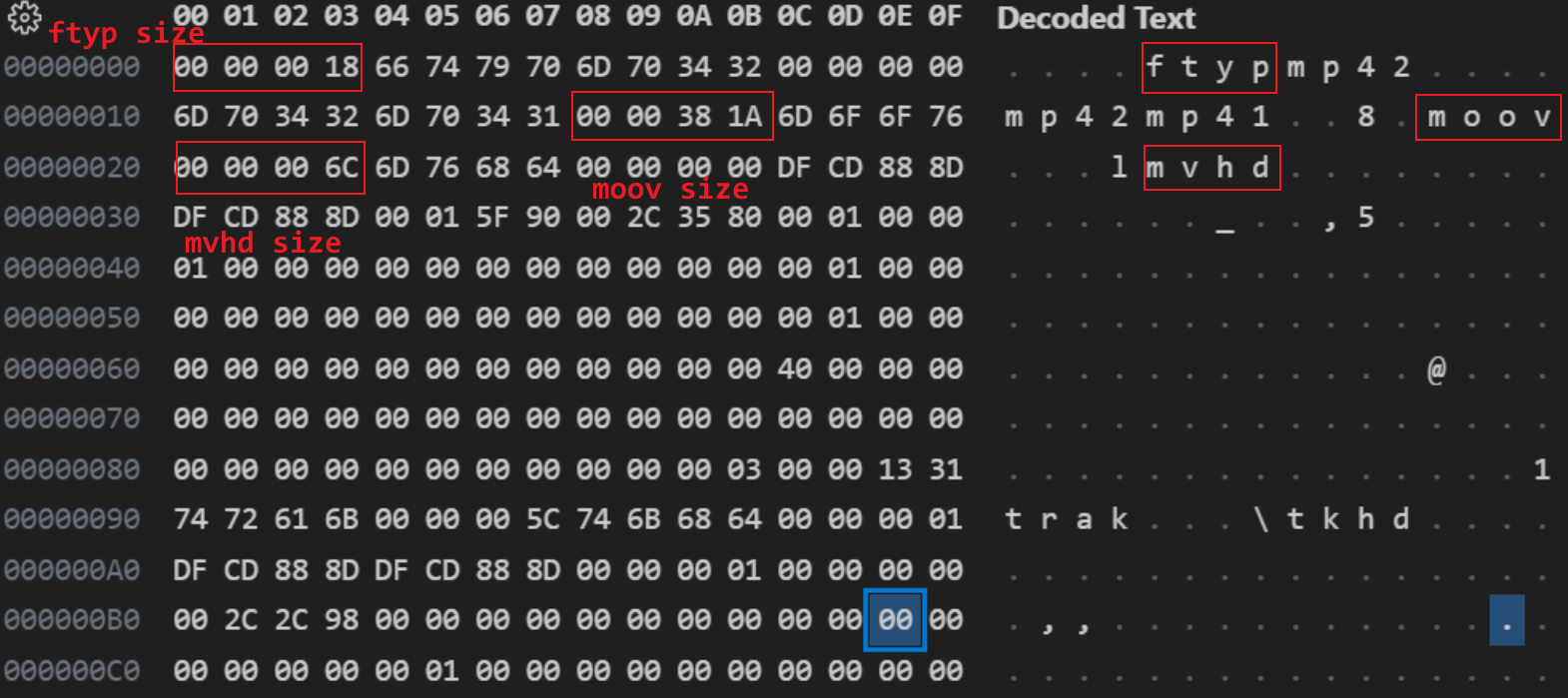
然后第一个ftyp box 是 0x18 字节大小,解析完第一个 box 就马上到 第二个box了,第二个box 的大小是 第 0x18 ~ 0x21 字节 ,第二个box 是一个 free box,自由发挥 box,可以自定义内容。以此类推不断解析。box 里面 可能会再套 box,也是同样的解析方法,
前面4字节是大小,后面 4 字节是 box 的类型。
分析到这里, mp4 的box结构就比较清晰了,很简单,前面4个字节是 size (大小),后4字节是 type (类型),box 里面的数据按照类型继续解析即可。
不过 size 有两个特殊值 0 和 1,请看下图。
- 当size等于0时,代表这个Box是文件的最后一个Box。
- 当size等于1时,说明Box长度需要更多的位来描述,在后面会定义一个64位的 largesize 用来描述Box的长度。

Box (Container)
然后我们再来介绍一下几个常见box的作用
- ftyp: Contains the file type, description, and the common data structures used.
- pdin: Contains progressive video loading/downloading information.
- moov: Container for all the movie metadata.
- moof: Container with video fragments.
- mfra: The container with random access to the video fragment
- mdat: Data container for media.
- stts: sample-to-time table.
- stsc: sample-to-chunk table.
- stsz: sample sizes (framing)
- meta: The container with the metadata information.
Here is a list of second-level atoms used in MP4:
- mvhd: Contains the video header information with full details of the video.
- trak: Container with the individual track.
- udta: The container with the user and track information.
- iods: MP4 file descriptor
下面对几个比较重要的表进行详细介绍:
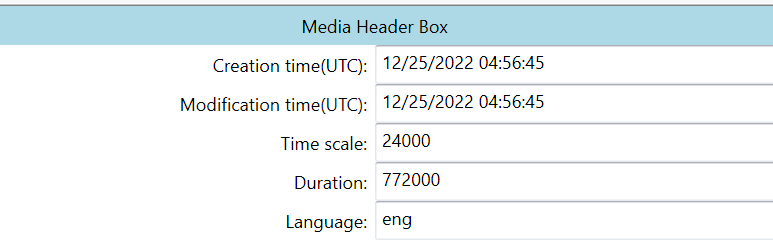
mdhd (Media Header)
stts (Sample To Timestamp)
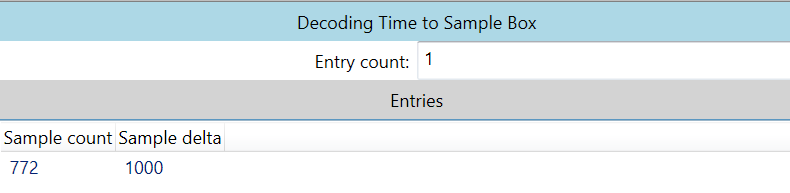
这个表的意思就是0-772帧的播放时间都是1000个time scale,也就是
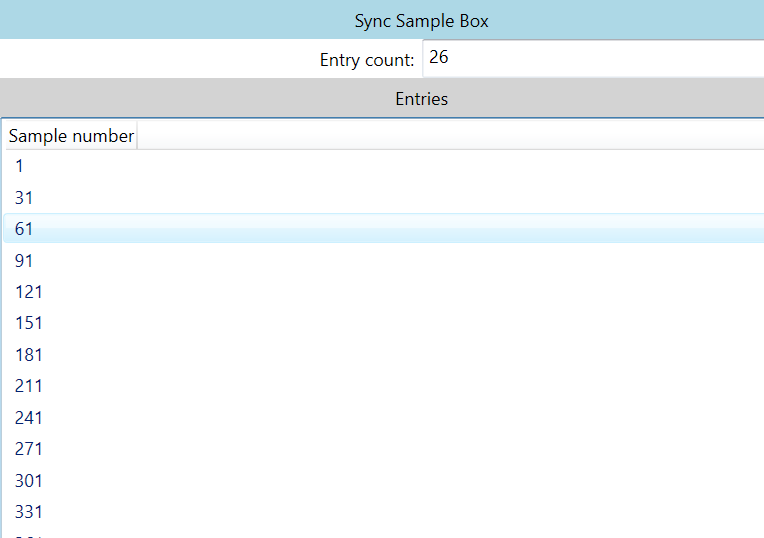
stss (Synchronize Sample)
这个是视频的关键帧表,也叫同步表,用来同步音视频
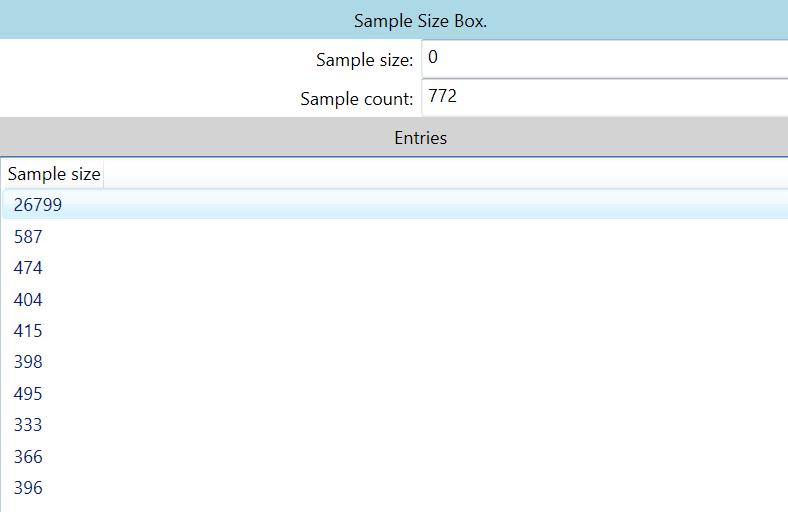
stsz (Sample Size)
这个是每个帧的大小,第一帧比较大是因为它是关键帧
stsc (Sample To Chunk)
帧映射到 chunk 的表。MP4 格式定义了 chunk,一个chunk 里面可以有 多个帧
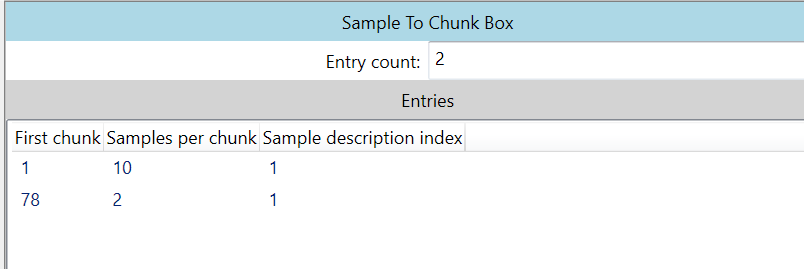
上图中有两行数据,不是说只有两个chunk,而是重复的数据被压缩,同样的套路。
上图中 第一行 的 First Chunk 是 1,Samples per chunk 等于 10,Sample description index 等于 1,意思是 第一个chunk 里面有 10个视频帧。
最后的 Sample description index 字段是指 第几个 Sample Description Box, 也就是 stsd 表,本文件只有 1个 Sample Description Box, Sample Description Box 有可能会有多个。
stsc 后面是省略的了,代表从 第78个 chunk 起,后面的每个chunk 都是只有2个视频帧。因为本视频流一共772帧,第一个chunk里面有10帧,后面的都是2帧,所以计算出来只有个chunk。
chunk 跟 sample 这个概念比较重要,MP4 索引定位找到某一帧,就是先找到chunk,再找到sample。
stco (Chunk Offset)
Sample 到 chunk 的映射了解完了,现在只要 找到 各个 chunk 的位置,自然就能找到 各个帧的位置,这个位置信息在 stco 表,全称 Chunk Offset Box,chunk的位置表,请看下图:
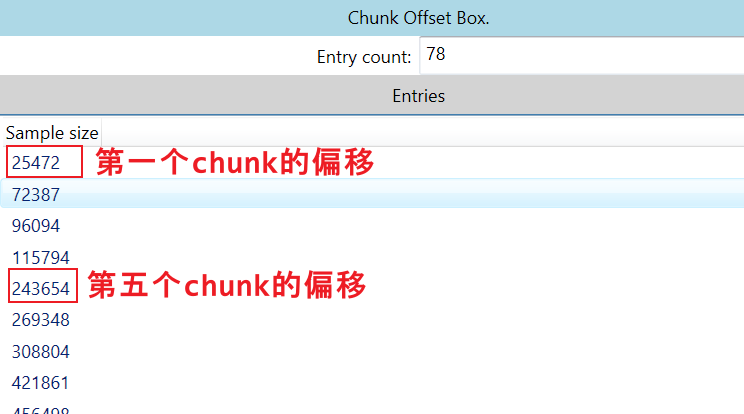
打开文件验证一下流的位置是否正确
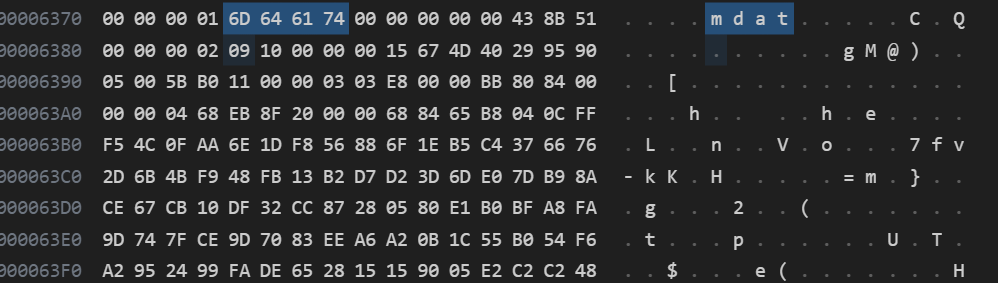
25472换算为十六进制为6380,从上图可以看到,0x6380 的地方,前面紧紧挨着 mdat,mdat之后的8个字节是这个box的大小,之前说过 mdat 是存储真正的音视频流的 box ,说明我们正确的找到了视频流的位置
分析 到这里 可以看出 MP4 与 FLV 的区别,MP4 除了 mdata box 是存储真正的音视频数据之外,其他的box都是辅助表,所以 MP4 有很强的编辑性,各种场景的数据查找的性能都很高。 FLV 更像一个 单向链表,你想要什么信息,只能遍历查找。 MP4不一样,你想查什么,我都整理好 放在各个 box 给你了。你不用遍历。所以MP4格式更像是加了很多索引的数据库,查起来很快。
一般来说,MP4中的音视频packet是交错排放的,这取决于每个track的STBL表
对比 MP4 跟 FLV 可以知道,音视频格式多种多种,FLV 没有 stsz 这个表,但是 FFmpeg 无论是解析 FLV,还是解析mp4,出来的 AVpacket 的size还是可以用的。所以FFmpeg 实际上就是对纷繁复杂的各种格式进行了封装,让编程更通用一点。
Pros and Cons
The MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14) file format is a widely used multimedia container format for storing audio, video, and other types of data. Like any technology, it has its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some pros and cons of the MP4 format:
Pros
- Versatility: MP4 supports a wide range of audio and video codecs, allowing for flexibility in terms of compression methods and quality.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: MP4 is widely supported across various platforms, operating systems, and devices, making it a versatile choice for sharing and distributing multimedia content.
- Streaming Support: MP4 is suitable for streaming content over the internet. It supports progressive download and streaming protocols, making it compatible with online video platforms.
- Metadata Support: MP4 supports the embedding of metadata, allowing for the inclusion of information such as title, author, and copyright details within the file.
- Chapter and Subtitle Support: MP4 supports chapter markers, making it useful for organizing content into chapters or segments. It also supports subtitles and closed captions.
- Compression Efficiency: MP4 files can achieve a good balance between file size and video quality, thanks to efficient compression algorithms. This makes it suitable for storing high-quality videos with reasonable file sizes.
Cons
- Not Standardized: MP4 is strictly speaking not a video format—it is a container format. It does not have a native method of processing media, so it relies on codecs. A media player must support these codecs to play an MP4 file. However, due to the huge popularity of MP4, many of its codecs have become standards themselves.
- Codec Compatibility: Codec compatibility issues can sometimes result in video being out of sync with audio.
- Intensive ability needed for encoding and decoding: Playback and editing of MP4 files requires significant processing power, because a file can contain several types of multimedia content and metadata.
- Compression Loss: MP4 compression results in good quality video, but it is still lossy. It is not a suitable choice for very high-definition video.
- Copyright: The convenience of the MP4 format has made it possible to illegally distribute copyrighted media content, which is a major problem for publishers.