Proxy Detection Websites
First, let's check the quality of your proxy environment. You can search online for proxy detection websites or use this detection site: link
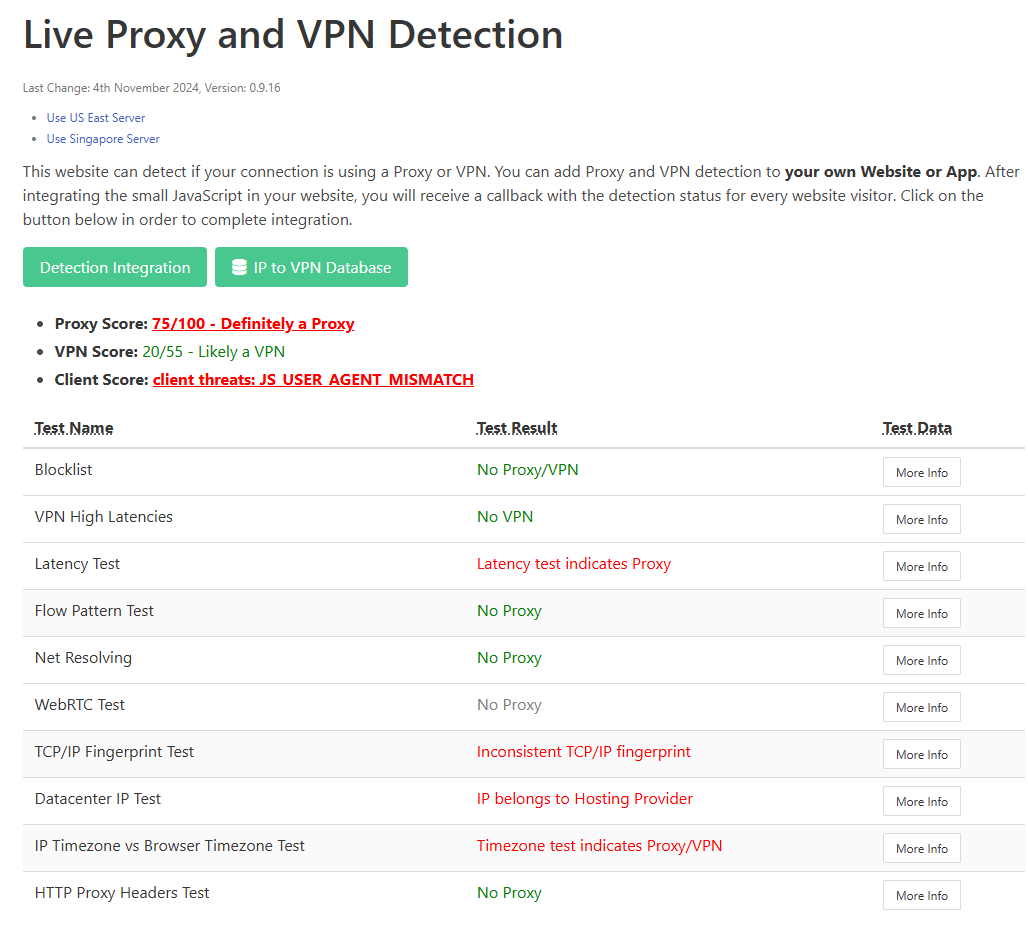
The image above shows my proxy detection results, which indicate that it has been identified as definitely a proxy. Now, let's go through each of these test items and learn how to bypass them.
Blocklist
As the name suggests, this refers to the IP blacklist maintained by the detection party. Different websites typically have different IP blacklists. If you're using a service like a VPN provider, it’s possible that others have used this proxy IP for malicious activities (like sending spam emails), resulting in that IP being added to the blacklist.
If this gets detected, the only option is to change your IP.
VPN High Latencies
This test checks if the user's latency is abnormally high, which is characteristic of VPN usage. However, I have never failed on this test, so I won't delve into it here.
Latency Test
This test determines latency by comparing TCP connection delays with WebSocket connection delays. The server can check the latency between itself and the proxy using TCP, and then measure the latency to the upstream host via WebSocket. Generally, these two connection delays should not differ significantly; a large discrepancy indicates proxy usage.
To bypass this test, use a proxy with a smaller latency that is geographically closer and has a better network environment.
Flow Pattern Test
This test assesses network traffic characteristics. Protocols like Shadowsocks, V2Ray, and Trojan can disguise themselves as HTTPS, and as long as the traffic is not in clear text, it usually passes the test without issues.
Net Resolving
Under normal circumstances, when resolving a non-existent domain, the response should immediately return DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN. An abnormal scenario occurs when a non-existent domain still receives an IP address, leading to a timeout when attempting to access that IP. Some proxies behave this way, but generally, I haven’t encountered this issue.
WebRTC
WebRTC operates over UDP traffic. If you only enable the system proxy or use a browser extension, it won’t take over the UDP traffic. In this case, discrepancies between the IPs for TCP and UDP traffic can lead to being identified as a proxy. The solution is to install a plugin that disables WebRTC or use a soft router and virtual network card to manage all traffic.
TCP/IP Fingerprint
If some OS characteristics of the proxy IP do not match the OS indicated in the HTTP User-Agent, it may also be identified as a proxy. For example:
{
"tcpIpHighestOs": "Chromium OS",
"userAgentOs": "Chromium OS"
}The server detects that the remote host is most likely Chromium OS based on the TCP connection characteristics. However, if a Windows machine's browser has a userAgentOS of Windows, it will then be flagged as a proxy. We can bypass this test by downloading a browser extension.
Datacenter Test
If your proxy IP provider utilizes hosting or other easily obtainable IPs, it might be identified as a proxy. For instance:
{
"asn": {
"asn": "xxx",
"abuser_score": "0.0021 (Low)",
"route": "xx.xxx.xxx.0/24",
"descr": "xxx",
"country": "xx",
"active": true,
"org": "xxx",
"domain": "xxx",
"abuse": "xxx",
"type": "hosting",
"created": "2023-xx-xx",
"updated": "2024-xx-xx",
"rir": "xxx",
"whois": "xxx"
}
}If the type field shows hosting, it indicates that your IP is provided by a VPS or another company, which could be flagged as a proxy. The solution is to find a proxy IP with the type field set to isp.
IP Timezone vs Browser Timezone Test
This test checks whether the timezone of the user’s OS matches that of the host. If they do not match, it will also be flagged as a proxy. Adjusting your OS's timezone can resolve this issue.
HTTP Proxy Headers Test
If the HTTP headers contain any information related to Proxy, it will be identified as a proxy. However, this would mean you’re essentially revealing your identity, and generally, these fields are not added to the HTTP headers.